BusWear alternatives and similar packages
Based on the "Android Wear" category.
Alternatively, view BusWear alternatives based on common mentions on social networks and blogs.
WorkOS - The modern identity platform for B2B SaaS

* Code Quality Rankings and insights are calculated and provided by Lumnify.
They vary from L1 to L5 with "L5" being the highest.
Do you think we are missing an alternative of BusWear or a related project?
Popular Comparisons
README
BusWear - EventBus for Android Wear

BusWear (:bus::watch:) is a simple library for EventBus to support Android Wear devices. Just adding one line of code lets you get synchronized event buses on Wear and mobile platform.
What is EventBus?
A great multi-purpose tool for Android apps, way of triggering some events in separate Activity, Fragment, Service etc. EventBus, origin of that project or Otto.
How to start?
To start with BusWear all you need is to add a dependency. That is it!
Add BusWear to your project
Gradle:
//library:
compile 'com.github.tajchert:BusWear:0.9.6'
//needed dependency:
compile 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-wearable:+'
Root build.gradle (due to Jitpack.io):
allprojects {
repositories {
...
maven { url "https://jitpack.io" }
}
}
How to use?
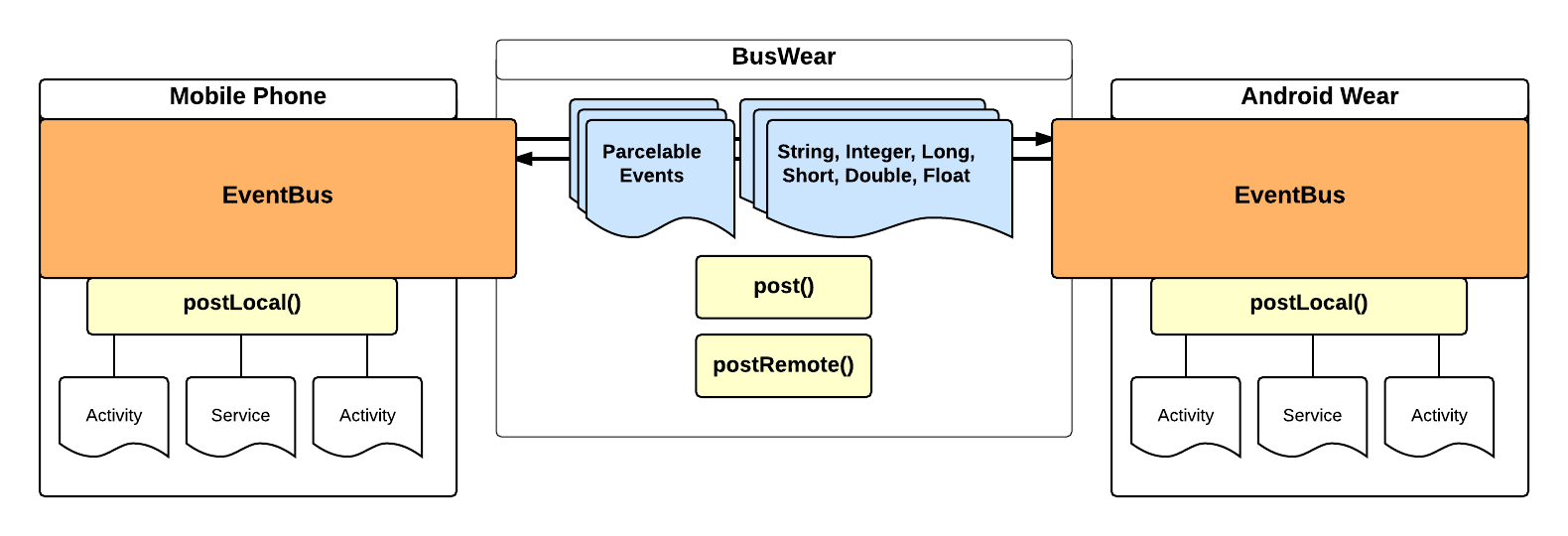
You can post to remote branch as long as it String, Integer, Long, Short, Float, Double or custom object that implements Parcelable, other "non-Parcelable" objects still can be posted but only locally.
post(object); sends your parcelable object (or String, Integer...) both to local bus and to remote one as well.
postLocal(object) works as old post() of EventBus, it sends event only locally.
postRemote(object) sends your parcelable object (or String, Integer...) to remote bus only.
The same goes for Sticky events - so you get postSticky(), postStickyLocal(), postStickyRemote(). Also methods such removeStickyEvent(Object), removeStickyEvent(Class), removeAllStickyEvents() work in same manner - you get everywhere, remote, local flavours of each method.
Sample
To send:
EventBus.getDefault(this).post(parcelableObject); //Custom parcelable object
EventBus.getDefault(this).postRemote("text"); //String
//... similar with Integer, Long etc.
EventBus.getDefault(this).postLocal('c'); //Character - to local function you can pass any object that you like
To receive:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
EventBus.getDefault(this).register(this);
}
//Called every time when post() is sent (with that particular object), needs to be annotated with the `@Subscribe` annotation.
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void onMyEvent(ParcelableObject parcelableObject){
//Do your stuff with that object
}
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void onMyOtherEvent(String text){
//Do your stuff with that object
}
//... more onXEvent() with @Subscribe annotation if you want!
Event propagation
Questions?
How is that better than classic EventBus?
EventBus works on mobile na Android Wear - yes, but you got two separate buses, and BusWear gives you a feel of one bus that is shared/synchronized between those two devices.
What are some drawbacks?
Probably quite big one is that all your custom objects to be posted needs to implement Parcelable (or be String, Integer...).
Other one is that you cannot have classes with same name in the same module (for example "wear") - it will lead to errors as matching is done on SimpleName of class.
License
BusWear binaries and source code can be used according to the [Apache License, Version 2.0](LICENSE).
Thanks
Goes to Polidea for putting me on a project that encouraged me to work on that library, Maciej Górski for Manifest merger, and Dariusz Seweryn for idea with Class name in path String.
*Note that all licence references and agreements mentioned in the BusWear README section above
are relevant to that project's source code only.


